Management of Flatfoot & High-Arched Feet
Foot structure plays a critical role in your overall mobility and comfort. Whether you have a collapsed arch or an excessively high arch, these structural variations can lead to pain, instability, and secondary foot conditions.
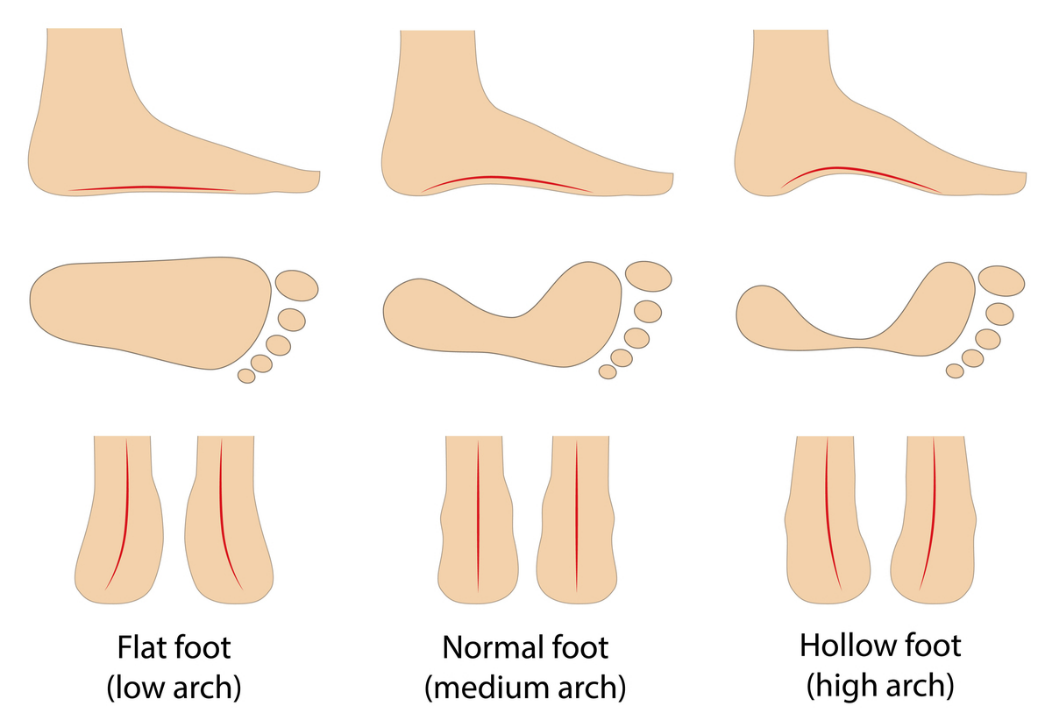
Understanding Flatfoot (Pes Planus)
Flatfoot is a complex disorder characterized by the partial or total collapse of the arch. This condition often results in “toe drift,” where the front of the foot points outward, and the ankle appears to turn inward.
Because flatfoot changes how weight is distributed, it can lead to:
- Achilles Tendinitis: Due to a tight Achilles tendon causing the heel to lift prematurely.
- Secondary Deformities: Such as the development of bunions and hammertoes.
- General Fatigue: Aching in the arches and heels after prolonged activity.
Managing High-Arched Feet (Cavus Foot)
A high-arched foot, or Cavus Foot, is a condition where an excessive amount of weight is placed on the ball and heel. This lack of foot flexibility often leads to instability and increased risk of ankle sprains. Symptoms can develop at any age and may affect one or both feet.
Clinical Assessment and Targeted Care
If you are experiencing discomfort due to your foot structure, professional intervention is key. Our Chiropodists specialize in biomechanical assessments to determine the specific nature of your foot type.
Our personalized management plans focus on:
- Custom-Made Orthotics: To redistribute pressure and provide structural support.
- Footwear Education: Guidance on selecting shoes that offer the necessary stability or cushioning for your specific arch type.
- Therapeutic Exercise: Stretching and strengthening protocols to address muscle imbalances.
The most appropriate management strategy depends on a thorough evaluation of your medical history and lifestyle. During your initial consultation, we will perform a comprehensive assessment to provide evidence-based recommendations tailored to your needs.
Take the first step toward improved foot function. Book Your Assessment Today






